| |
Poor spheroidization is very harmful to ductile iron castings. The following describes the causes of this phenomenon, performance characteristics and preventive measures.
The main reasons for poor spheroidization are:
-
The amount of intermediate alloy is not enough during the spheroidization reaction: the amount of alloy added is small;
-
The amount of spheroidizer is appropriate, but the sulfur content in the molten iron is high;
-
The molten iron is oxidized, resulting in magnesium burning and insufficient spheroidizer content, etc.
Measures to be taken to prevent poor spheroidization in production:
-
Strictly control the sulfur content of the original molten iron, and low-sulfur pig iron should be used;
-
During spheroidization, magnesium should be prevented from burning as much as possible to increase the absorption rate of the spheroidizing agent;
-
The spheroidizing agent should be added in sufficient amount;
-
The molten iron temperature should be controlled within the range of process requirements. If the molten iron temperature is too low, the alloy is easy to "keep", and if the temperature is too high, the spheroidizing agent will burn too much, which will cause poor spheroidization.
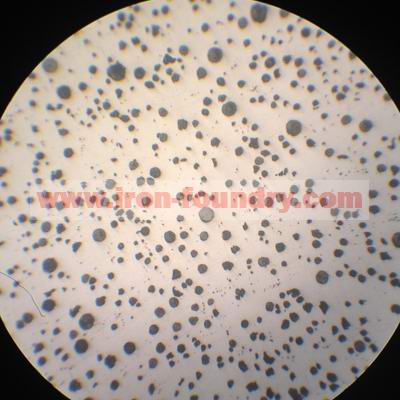
Good Spheroidization of Ductile Iron |
|
