Grey Iron vs. Nodular Iron
Many people will wonder the differences
between grey iron and nodular iron, this article is intended to
introduce the grey iron and nodular iron in microstructure, physical
properties and chemical composition.
1. Microstructure
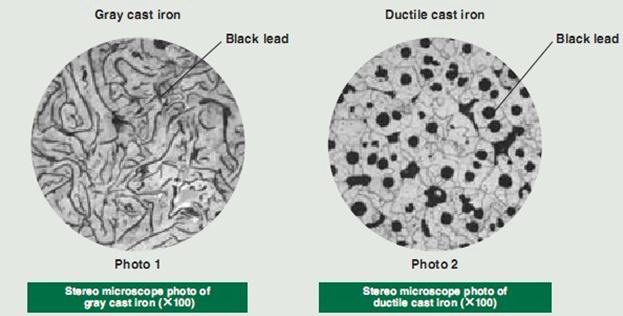
The key feature of grey iron is that it includes flakes of graphite
which develop during the cooling process. These graphite flakes give
grey iron a distinctive gray color when it is fractured, and they
are also involved in many of the physical properties of this iron
alloy.
The microstructure of nodular iron is the
discrete form of the graphite nodules. Nodular iron is created by an
alloying process, which converts the crack-promoting graphite flakes
of gray iron into nodules. With this micro-structural
transformation, the metal acquires superior ductility and elongation
characteristics.
2. Physical Property
Compared with grey iron, nodular iron has an absolute advantage in
intensity. The max tensile strength of nodular iron is 90k psi,
while the max tensile strength of grey iron is only 35k psi.
Nodular Irons are generally superior to
grey irons, regarding their yield strength. The max yield strength
of ductile iron is 40k psi; Grey iron is not very malleable or
strong, it fractures easily.
Nodular iron is more flexible and elastic
than other cast irons. Nodular iron has higher strengths, greater
elongation and better resistance to impact than grey iron.
The nodular iron family offers the design
engineer a unique combination of strength, wear and fatigue
resistance and toughness as well as excellent ductility
characteristics. In all its grades, nodular iron exhibits mechanical
properties that make it an ideal materials for mechanical and
automotive parts.
Gray iron is the most versatile of all foundry metals. With the
exception of wrought steel, grey iron is the most widely used metal
for engineering purposes. Grey iron is an extremely inexpensive
metallic material and is readily available in large quantities at
almost any foundry.
3. Chemical Composition
|
Chemical composition
|
Cast Iron Material |
|
Grey iron (%) |
Nodular iron (%) |
|
C |
2.9~3.5 |
3.5~3.8 |
|
Si |
1.4~2.1 |
2.0~3.2 |
|
Mn |
0.6~1.0 |
<0.5 |
|
P |
0.1~0.5 |
<0.08 |
|
S |
0.1~0.12 |
<0.025 |
|
Mg |
|
0.03~0.06 |
|
RE |
|
|
The different chemical composition of grey
iron and nodular iron directly determines their different
properties. After reading the above analysis, we hope your can get a
better understanding about grey iron and nodular iron.
Home |
More Articles |
